Utilising free databases for research on Indian Law
Legal Tech, Datasets ·Table of Contents:
- Sample Research Topic Number 1: Scope of challenge to arbitral award at the enforcement stage
- Sample Research Topic Number 2: Law relating to disposal of E-Waste
- Database for Environmental Law notifications
- An in-development version of the web-app
In my previous post, I had provided a list of freely accessible resource lists, maintained by Indian and international institutes.
One may have some hesitancy to use these freely accessible resources in their research workflow, owing to the fact that these sources mostly function as lists of information that have not been indexed in a database anywhere, as far as I know. However, I am attempting to solve this problem (see bottom of page for a link)
These freely accessible sources can augment if not fully replace your research workflow if you have familiarity with their content, and this is what I want to demonstrate in this blog post.
Sample Research Topic Number 1: Scope of challenge to arbitral award at the enforcement stage
For anyone familiar with arbitration law, this is a familiar headache that can be approached from as many points of view as the arbitration act affords opportunity for recourse through.
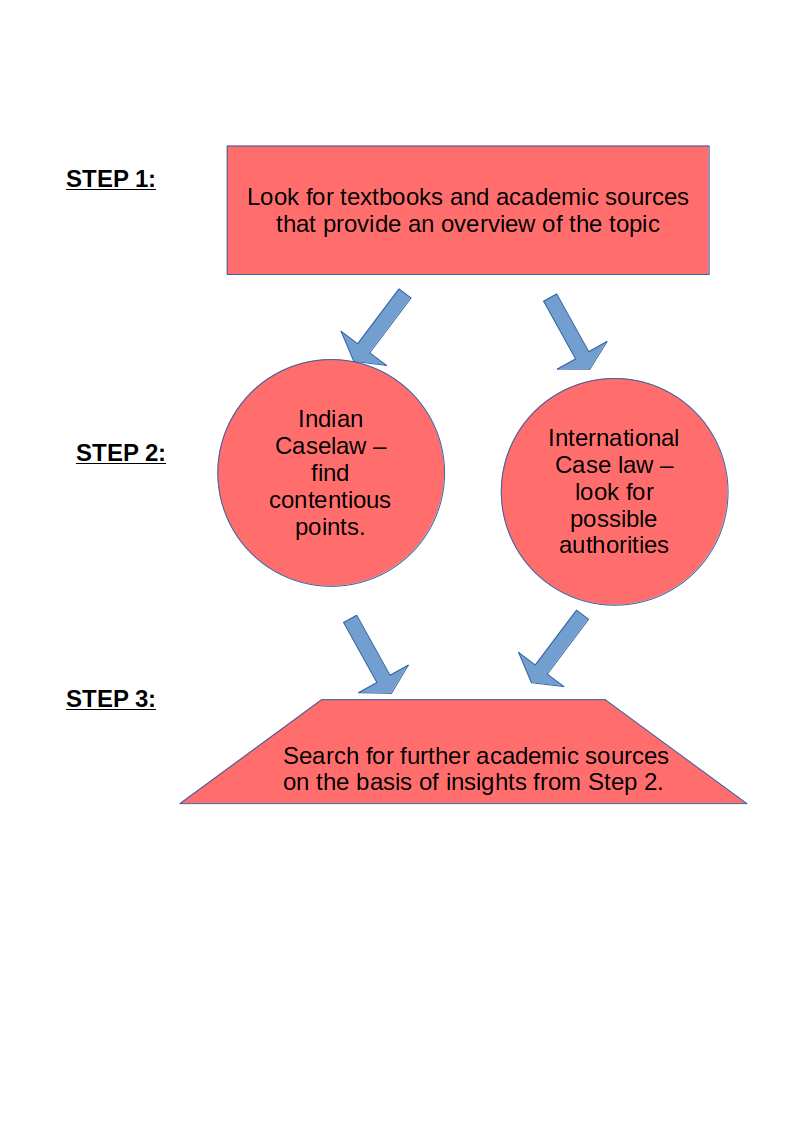
Step One:
One must begin with Section 34 of the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996 which provides a list of grounds on which the arbitral award may be challenged.While the text of the oft-amended and discussed section can be found on IndiaCode, one must be cognisant with the discussion around the arbitration regime to know at which stage Section 34 exists, with respect to other reliefs.
This can be gathered from the sources which contain textbooks and academic literature. Knowing that Alternate Dispute Resolution is a key part of the focus of judicial academies, their online resources would be beneficial in this regard.
Here is what I found as regards basic reading material that will inform a deeper dive based on the groundwork laid by reading these texts:
1. e-Book- Handbook on Arbitration Law by Justice S.U.Khan
2. Honourable Justice R.D Dhanuka's lecture on the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996 and important cases from the Bombay High Court Judges' Library
3. ADR and Access to Justice by Honourable Justice S.B. Sinha
Hence, so far a researcher would know about the statutory grounds for challenge, and some basic academic literature that comments on the statutory provisions with the landmark cases
Step Two:
Preferable course of action is to locate caselaws similar to the research proposition. To further demonstrate the applicability of the law to a particular case at hand, one can utilise the freely accessible journals at this step.
1. Indian caselaws can be located through a keyword search on e-SCR. This would involve filtering by the Act name and Section number after proceeding to the keyword search result screen. This has a list of judgments with headnotes selected officially for their relevance.
2. For a further search of the caselaws one may opt to search at the Legal Information Institute of India.
3. International precedents under the UNCITRAL Model Law implementing countries are available on the Case law on UNCITRAL texts CLOUT, where one can sort by the legislative text . One will have to filter by article number on CLOUT by selecting it from the drop down filters.
Step Three:
Having found the caselaw in national and international contexts, one can also supplement the understanding of the caselaw by locating academic journals. To locate these journals, one can use the information obtained from the caselaws to define the keywords or titles that one is looking out for.
In the instant case, having found about the "public policy", "patent illegality", and "fundamental policy of the law" as being aspects that are contentious issues in deciding the arbitral award's challenge, one can then use these keywords as search terms in journal websites. These journal articles can be found from journal indexes such as:
1. Articles in The Indian Arbitration Law Review that was found via search on the Electronic Journals Library .
2. Articles from journals indexed in the Law Review Commons such as this one(click here) that deals with public policy .
Sample Research Topic Number 2: Law relating to disposal of E-Waste
Owing to the onus of policymaking and governance in India focussing on waste disposal and recycling, there has been a push towards creation of a rules and regulations regime for meeting these policy objectives.
Hence, treating the ascertainment of such rules and regulations as regards treatment of different categories of waste:- say electronic waste, plastic waste, and bio-medical waste is a common research proposition that involves looking through Indian government websites.Step One:
A good place to start for this proposition would be with the published literature that summarises the content as we did for Sample Research Topic Number 1, above.This content can be found on a number of portals, such as:
1. Owing to the availability of a large corpus of theses that summarise the policies of the Indian government, Shodhganga would be a good starting point, where I found theses such as this one (click here) by researcher Shambhu Kumar Gupta at Patna University that deals with the legal regime for electronic waste, from many different points of view.
A word of caution: the website loads a little slowly, so you may have to take what you get in the first few searches. 2. The topic being one with respect to which substantial academic literature was found, the Self-Learning Material on e-Gyan Kosh can also be searched for accessing content in this regard. Here, selecting the Self-Learning Materials category from the drop-down filter allows you to filter by text materials only. This is where I found a textual guide for managing hospital waste which is part of the course material for IGNOU's Post Graduate Diploma in Hospital and Health Management.
Step Two:
Having identified the basic legal regime in terms of the rules and regulations disseminated in academic literature, it is key to then utilise the Ministry websites, since this is a diversified regime across many sectors (for instance, Electronic waste disposal is simultaneously the responsibility of the Central and State Pollution Control Boards, as well as Municipal Corporations under the E-Waste (Management and Handling) Rules, 2011).
Hence, the following websites are instrumental in locating the compliance requirements
1. The website of the Ministry of Environment Forests and Climate Change is instructive in this regard. Specifically, if one navigates to the archived orders , one can locate the relevant rules from this section, such as the Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016, and the E-Waste management rules, 2016, with the amendments made thereon.
2. Additionally, the website of the Central Pollution Control Board has resources that provide a list of archived reports, guidelines on waste disposal, and varying other notified orders and documents.
3. There are various portals that the Indian Government maintains such as the "Parivesh" portal for Environmental Clearances, and the Climate Change Knowledge Portal.
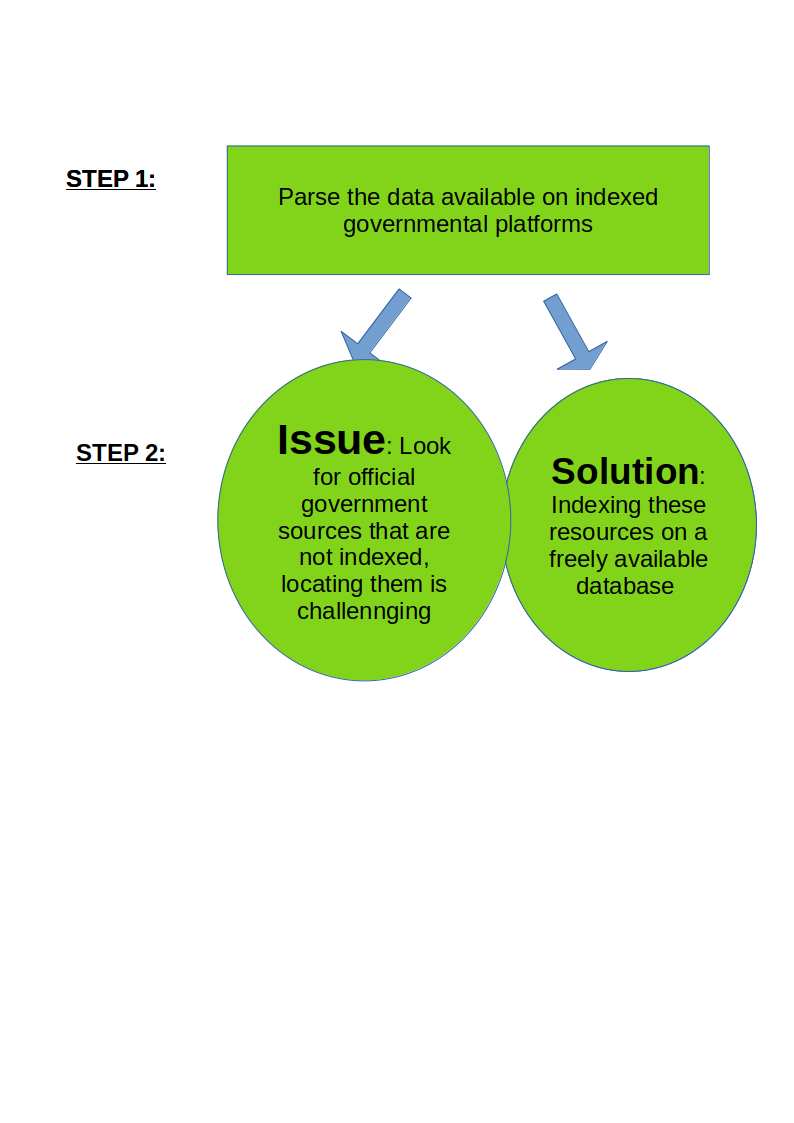
This proves to be a cumbersome research process, how do I make it simple?
There are various problems faced while traversing through the vast trove of Ministry websites and sources, such as:
- Unavailability of a list of archived resources.
- Search features on websites (such as the government website portal India.gov.in) being not fully representative of actual resources available.
- A singular access point for searching multiple websites.
Solution - a minimal web-app for searching freely available Indian environmental law resources
To solve the problems related to accessing information, I think it best to make a web app that provides links to the resources available freely. I do not intend to reproduce the assets as a traditional proprietary database, rather provide hyperlinks and navigation instructions for every resource that can be browsed on the web app.